Building Halodoc's AI Orchestration Hub Using MCP
At Halodoc, our engineering environment is complex and ever-growing. We use Jenkins for CI, Kubernetes for clustering and deployments, New Relic for monitoring and several in-house platforms for domain-specific data. Each of these tools is powerful on its own, but the real challenge shows up when engineers need to troubleshoot issues across different domains; whether it’s a failed pipeline, a degraded application, a resource bottleneck or an unexpected metric spike.
Today, debugging requires jumping between multiple systems. For example, if a Jenkins pipeline fails, the first instinct is to dig through console logs. If that points to a Kubernetes problem, the next step involves switching to the terminal and running kubectl commands. If the trail leads to an application crash, New Relic becomes the go-to place for traces and error logs. And often, to complete the picture, engineers also query internal data platforms for custom metrics or operational data.
This fragmented workflow results in constant context switching, repeated manual effort and slower resolution times. The bigger issue is that no single tool provides a holistic view of the problem.
Large language models (LLMs) can help here, but there’s a catch. While they are extremely competent on their own, their knowledge is limited to training data. They need real-time, contextual information like Jenkins job data, Kubernetes state, application traces or domain-specific metrics to provide actionable insights. Traditionally, AI has been connected to these external systems in a fragile, one-off way, requiring custom scripts or plugins for every integration.
To overcome this, we built what we call the AI Orchestration Hub: a single entry point into our engineering ecosystem powered by the Model Context Protocol (MCP). The hub doesn’t just analyze deployment issues it can fluidly move between examining CI failures, inspecting Kubernetes resources, analyzing application performance, correlating logs or even querying internal databases for custom metrics. And it does all this while enforcing security through RBAC.
In this blog, we’ll explore the architecture behind this hub, how it ties into existing systems and the safeguards that ensure it stays secure and dependable.
Why This Matters for Engineers
- For New Joiners: No more waiting for lengthy knowledge transfers. With AI guidance, they can query and understand systems in one place, speeding up onboarding and learning by doing with built-in guardrails.
- For Senior Engineers: Free from routine operational overhead, they can focus on architecture, scalability, and solving complex problems that drive long-term improvements.
- For Cross-Team Collaboration: Standardized AI-driven workflows make operational knowledge easily shareable, reducing silos and enabling smoother collaboration across various teams.
- For Knowledge Preservation: Tribal knowledge no longer stays locked in individual heads; it’s captured, systematized, and made accessible through AI-powered procedures.
AI Orchestration Hub Architecture:
Our AI Orchestration Hub follows an intelligent architecture designed for autonomous reasoning, secure execution and cross-domain intelligence.
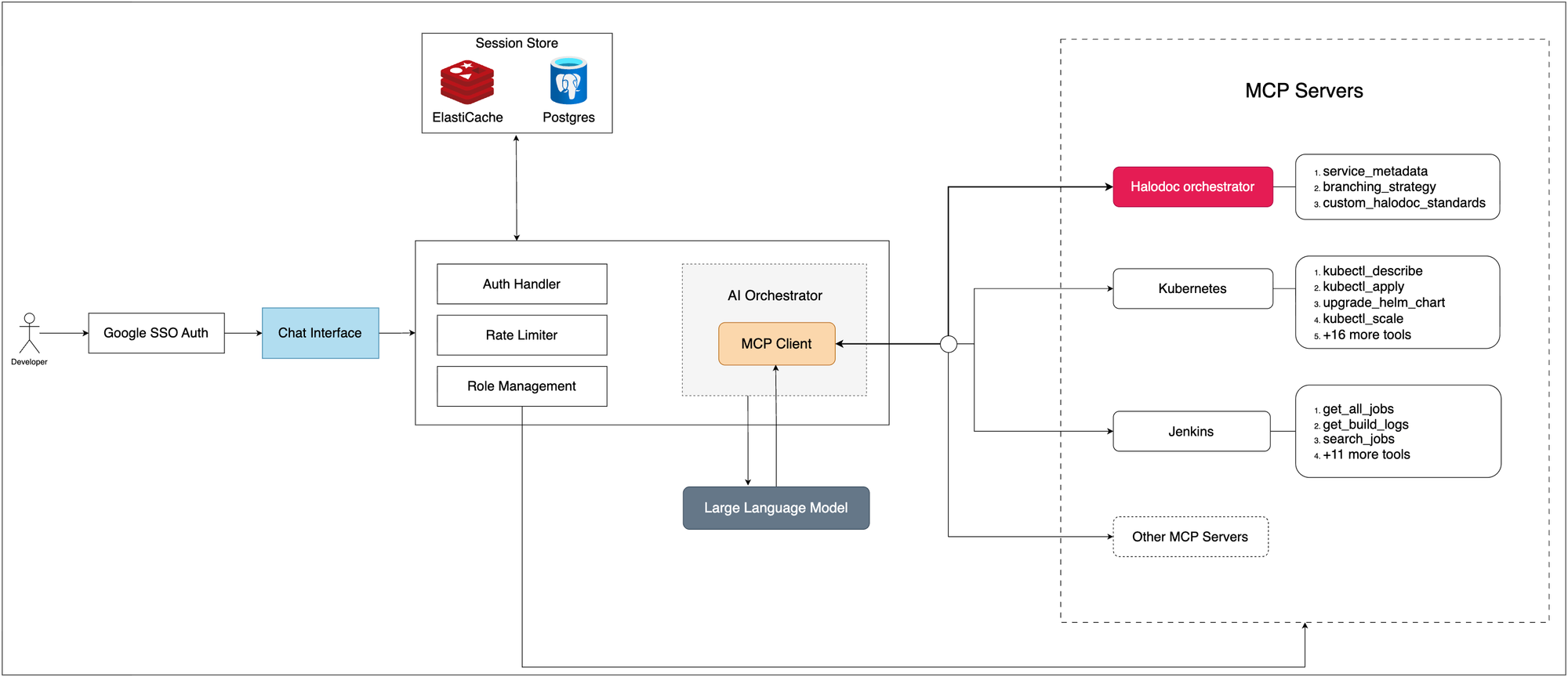
Frontend User Interface
Our frontend provides a conversational interface that's immediately familiar to developers while hiding the complexity of multi-system integrations. Key features include:
- Google SSO Authentication: Complete access control. Without Google login authentication, users cannot access the chat interface.
- Session Management: Persistent chat history and context preservation across browser sessions
- Real-time Interactions: Immediate feedback during tool executions and multi-step operations
The React-based frontend communicates exclusively through RESTful APIs, ensuring clean separation between presentation and business logic layers.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in MCP
While Google SSO secures who can access the platform, RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) defines what each user is permitted to do once inside. In MCP, RBAC plays a critical role because it directly governs the tools an LLM can invoke.
The LLM itself doesn’t understand permissions; it simply chooses from the tools available to it. By exposing only the allowed tools per user, RBAC ensures fine-grained security and controlled execution.
Why RBAC Matters
- Example 1:
- Available tools:
[kubectl_get, kubectl_create, kubectl_logs] - Request: “Please create a pod 'ABC' in 'XYZ' namespace.”
- Outcome: The LLM uses the
kubectl_createtool to fulfill the request.
- Available tools:
- Example 2:
- Available tools:
[kubectl_get, kubectl_logs] - Request: “Please create a pod 'ABC' in 'XYZ' namespace.”
- Outcome: No action is taken, as
kubectl_createis not available to this user.
- Available tools:
RBAC Enforcement Model
- Database-backed rules: Each user’s email is mapped to a set of blocked tools.
- Dynamic exposure: AI Orchestrator checks RBAC rules before exposing tools to the LLM session.
- Execution safety: LLM can only instruct to execute the tool which are within its scope only.
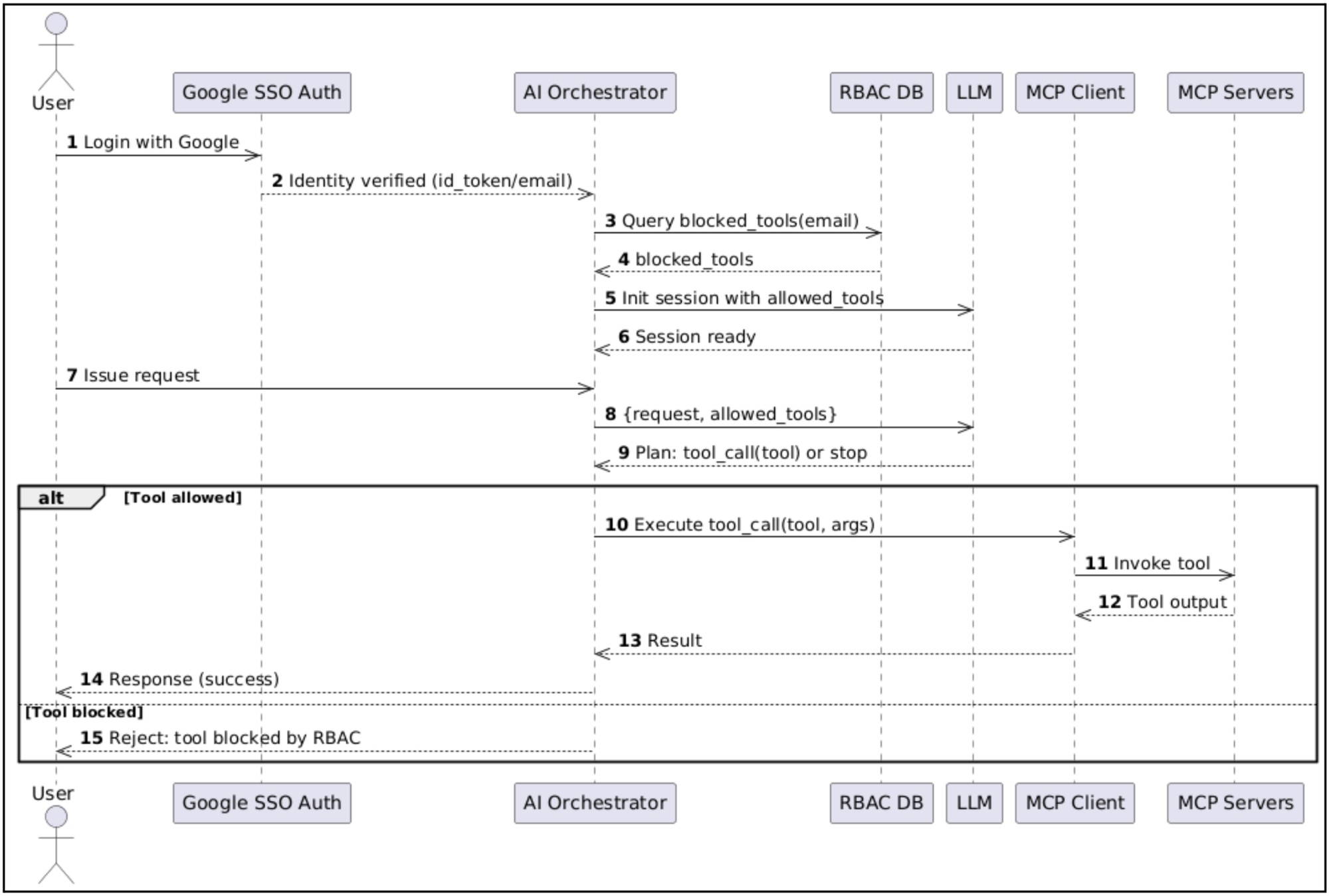
Request Flow:
AI Orchestrator - The Integration Brain
The AI Orchestrator serves as the universal translation layer between human intent, AI reasoning, and operational systems. This component handles the most complex aspects of our platform. Built with FastAPI, it uses a hybrid chat history storage design that combines ElastiCache for short-term memory and PostgreSQL for long-term memory, ensuring high performance and reliability. The system is powered by OpenAI’s GPT-4.1 model.
At the core of the system is MCP. Think of MCP as a universal adapter for the AI assistant. Our tools Jenkins, Kubernetes, New Relic and others are like devices with different plugs. Instead of building custom connectors for every possible combination, MCP acts as the bridge between LLMs and these systems. By providing a consistent protocol, it removes duplication, accelerates adoption and ensures AI integrations remain scalable and easier to maintain over time.
AI Orchestrator Functionality
Session Initialization: The session creation flow demonstrates our platform's sophisticated initialization.
- MCP Server Discovery: Query all available MCP servers for current status
- Connection Establishment: Create persistent connections to all discovered servers
- Tool Enumeration: For each active server, retrieve the complete tool catalog
- User Context: Apply RBAC filtering to limit available tools based on user permissions
- Session Persistence: Store session metadata in Postgres with ElastiCache
Conversational AI with Tool Execution
In our Conversational AI setup with tool execution, every user request first passes through a token validation step. Each user is assigned a fixed token quota and before the query is processed, the system checks whether their usage is within the allowed limit. If the quota is exceeded, the request is rejected immediately; otherwise, the query is forwarded to the AI Orchestrator along with the active session context.
Request flow:
- Check token quota: read used_tokens for the user, compare with allowed_tokens, and stop with a “quota exceeded” error if the limit is surpassed; otherwise continue.
- Load session context: if session_id is missing in ElastiCache, fetch chat history from Postgres and cache it in ElastiCache for low-latency reuse.
- Call the LLM: Provide the user_query, including the available MCP tool registry and current session_chats as context so the model can decide whether to respond or call a tool in its loop.
- Update token usage: read tokens from the API response usage field, increment persistent counters, and sync used_tokens to Postgres for durability and reporting.
- Handle LLM response: append the user_query and assistant message to ElastiCache and Postgres, and branch on response type (stop vs tool_call).
- If tool_call: execute the requested MCP tool, capture output, add it as an assistant message, and iterate the LLM loop up to a configurable max (e.g., 10).
- Return response: when the model stops, return the final assistant message to the caller.

This recursive execution pattern enables complex multi-step operations while maintaining full context awareness throughout the entire workflow.
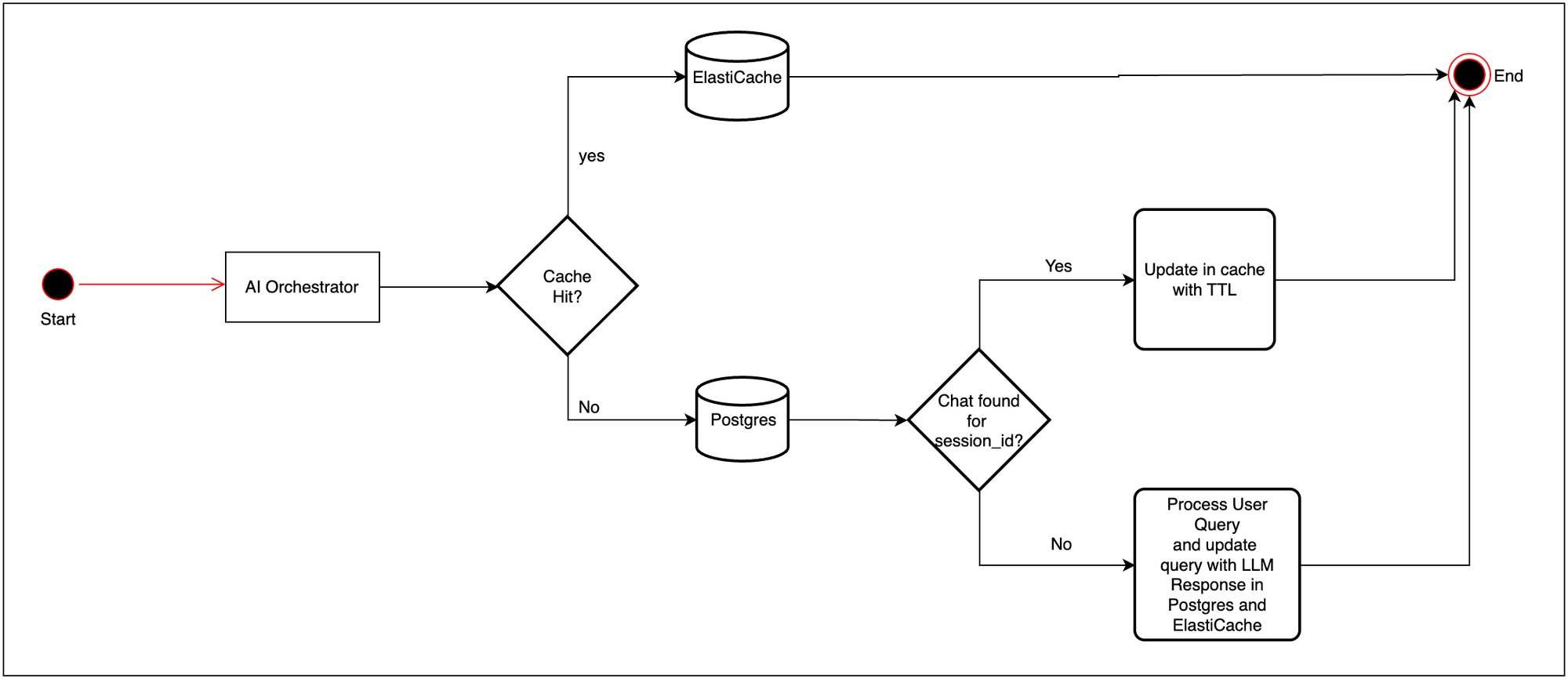
Advanced Chat History Management
Our Postgres + ElastiCache hybrid architecture provides:
- Fast access to active conversations through memory caching
- Persistent storage for long-term conversation history and audit trails
Automatic failover from memory to the database when sessions are cold
MCP Servers - Pluggable Operational Capabilities
Our platform is plug-and-play in nature. Instead of building everything from scratch or locking ourselves into one way of doing things, we keep it simple with a configuration file. If we want to bring a new MCP server on board, all it takes is a quick config update, no major rewrites, no messy integrations.
What’s even better is the freedom it gives us. These servers can be open-source tools that many teams already know and trust, or custom-built ones designed for our unique needs. That flexibility means we’re never stuck, we can pick the right tool for the job, and swap things in or out as our requirements evolve.
In practice, this design makes life easier. Whether we need new capabilities for monitoring, automation, or observability, they can be plugged in without disrupting the whole system. It keeps the platform lightweight, adaptable, and ready for whatever comes next.
{
"mcpServers": {
"kubernetes": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"mcp-server-kubernetes"
],
"env": {
"ALLOW_ONLY_NON_DESTRUCTIVE_TOOLS": "true"
}
},
"Jenkins": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"mcp-remote",
"http://127.0.0.1:9887/sse/",
"--allow-http"
]
},
.
.
.
}
}MCP Server Config file
Conclusion
At Halodoc, building AI Orchestration Hub with MCP wasn’t just about connecting tools; it was about rethinking how engineers interact with complex systems. By putting authentication and RBAC at the core, we ensure that every interaction is not only intelligent but also safe and controlled.
What started as an effort to reduce context-switching has turned into something much bigger:
- A platform that helps new joiners learn the ropes faster
- A productivity boost for senior engineers by offloading repetitive tasks
- A way to preserve knowledge and make expertise more accessible across teams
- And ultimately, a system that makes day-to-day engineering smoother and more collaborative.
We’re just scratching the surface of what AI can do. With MCP as the universal bridge and AI as the thinking layer, the possibilities for scaling engineering knowledge and operations are endless.
The future we see is one where engineers spend less time wrestling with tools and a lot more time solving problems that truly matter.
References:
Building MCP Server
Building MCP Client
Open source MCP servers
Join us
Scalability, reliability, and maintainability are the three pillars that govern what we build at Halodoc Tech. We are actively looking for engineers at all levels and if solving hard problems with challenging requirements is your forte, please reach out to us with your resumé at careers.india@halodoc.com.
About Halodoc
Halodoc is the number one all-around healthcare application in Indonesia. Our mission is to simplify and deliver quality healthcare across Indonesia, from Sabang to Merauke. Since 2016, Halodoc has been improving health literacy in Indonesia by providing user-friendly healthcare communication, education, and information (KIE). In parallel, our ecosystem has expanded to offer a range of services that facilitate convenient access to healthcare, starting with Homecare by Halodoc as a preventive care feature that allows users to conduct health tests privately and securely from the comfort of their homes; My Insurance, which allows users to access the benefits of cashless outpatient services in a more seamless way; Chat with Doctor, which allows users to consult with over 20,000 licensed physicians via chat, video or voice call; and Health Store features that allow users to purchase medicines, supplements and various health products from our network of over 4,900 trusted partner pharmacies. To deliver holistic health solutions in a fully digital way, Halodoc offers Digital Clinic services including Haloskin, a trusted dermatology care platform guided by experienced dermatologists.We are proud to be trusted by global and regional investors, including the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Singtel, UOB Ventures, Allianz, GoJek, Astra, Temasek, and many more. With over USD 100 million raised to date, including our recent Series D, our team is committed to building the best personalized healthcare solutions — and we remain steadfast in our journey to simplify healthcare for all Indonesians.




